
Hair loss is one of the most common and rapidly increasing sign of today’s highly stressful and demanding life-style. The total number of hair on human head is approximately between 1.0 – 1.5 lacs. It is normal to lose 50-100 hair every day during head-bath and combing, but if you start losing more than 100 strands per day, hair loss becomes significant and needs attention. It can be very distressing and can lower your self-confidence. Hair loss can affect men, women and children.
To understand why and how hair loss occurs, first you need to understand the normal hair growth cycle. The hair growth depends on many factors like genes, age, hormonal effects and sickness.
Hair Growth cycle: Each hair passes through following 3 stages of hair cycle:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): It lasts 2-6 years and approximately 85% of all hair are in the growing phase at any one time. On an average, human hair grows approximately ½ inch per month.
- Catagen (Transitional phase): It lasts 2-4 weeks and the hair follicle shrinks to about 1/6 of the normal length.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): It lasts 5-6 weeks and approximately 10-15% of all hair are in this phase at any one time. At the end of the Telogen phase, the hair follicle re-enters the Anagen phase and a new hair begin to form. If the old hair has not already been shed the new hair pushes the old one out and the growth cycle starts all over again.
This means that each hair grows for 2 to 6 years, then rests, and then falls out. A new hair soon begins to grow replacing the fallen one. Baldness occurs when hair falls out, but new hair does not grow in its place.
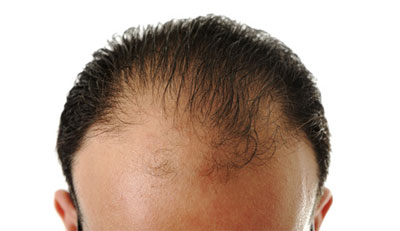
What causes excessive hair loss?
A number of factors can cause hair loss which may be temporary or permanent.
Temporary Hair Loss: It can happen after taking some medicines, exposure to chemicals, hormonal and nutritional factors, thyroid disease, pregnancy, after radiation and chemotherapy. Stress is another big factor in today’s competitive world. Hair Styling, excessive use of cosmetic products and infections of the scalp can also cause hair loss. But this type of hair loss is usually reversible, after the underlying cause is treated or removed.
Permanent Hair Loss (Androgenetic alopecia): Though much more common in men, it can be seen both in males and females.
Male-pattern baldness: is the most common cause of hair loss in men. It is due to the sensitivity of hair to male sex hormone ‘testosterone’ and is very common in those who genetically inherit this trait. In these individuals, testosterone destroys the cells responsible for the growth of hair roots. These hair first get thinner and weak, then stops getting longer, finally die and fall down. Men who start losing their hair at an early age tend to develop more extensive baldness. In male-pattern baldness, hair loss typically results in a receding hair line and baldness on the top of the head, but the hair at sides and back of scalp are not sensitive to the effects of testosterone.
There are many classification system used to categorize the extent of baldness. However, the most widely accepted standard is the Norwood classification for male-pattern baldness.
| Type | Illustration | Definition |
|---|---|---|
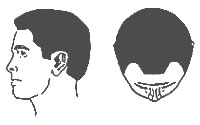
| Type I |
|
Minimal or no recession of the hair line. It represents an adolescent hairline and is not balding. |
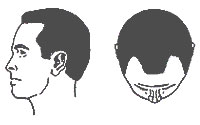
| Type II |
|
It is triangular, usually symmetrical, areas of recession at the fronto-temporal hair line. It represents adult or Mature hairline and is not actually balding. |
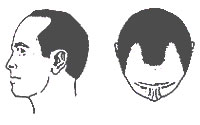
| Type III |
|
It is the earliest stage of male hair loss. It is characterized by a deepening temporal recession. |
| Type III Vertex |

|
It represents early hair loss in the crown (vertex) with limited recession of the fronto-temporal hair. |
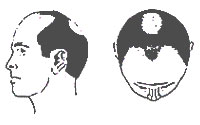
| Type IV |
|
There is further frontal hair loss and enlargement of vertex, but a solid band of hair across top separating front and vertex still remains. |
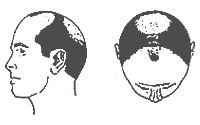
| Type V |
|
The bald areas in the front and crown enlarge further and the bridge of hair separating the two areas begins to break down. |
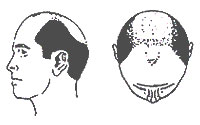
| Type VI |
|
The connecting bridge of hair disappears leaving a single large bald area on the front and top of the scalp. The hair on the sides of the scalp remains relatively high. |
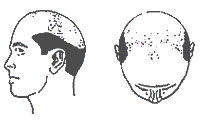
| Type VII |
|
Extensive hair loss with only a wreath of hair remaining at the back and sides of the scalp which also become very fine. This is the most severe form of hair loss. |
Female-pattern hair loss (FPHL) is a term given to androgenetic alopecia in females or female-pattern baldness. It is mainly of 2 types – Diffuse hair loss and Localized hair loss. It can be of scarring and non-scarring types. Majority of the females present with diffuse, non-scarring type of hair loss. It may be hereditary and is usually due to the change in levels of male hormone (testosterone) and is the most common cause of hair loss in women as well. It is often seen in women after menopause, but can also occur even in much younger women. Women get hair loss on the front and top of the scalp, but the frontal hairline is preserved (this is opposite to male-pattern baldness who always have receding or loss of frontal hairline). This condition is usually progressive, if not treated. The back and sides may or may not be involved. Rarely females become totally bald like men.
Before offering any treatment plan for FPHL, it is very important to carefully examine and investigate each woman to rule out any underlying hormonal or medical problem responsible for hair loss.
FPLL is classified based upon the degree of thinning (Ludwig classification). The Ludwig Classification uses three stages to describe female pattern genetic hair loss:
| Type | Definition | Illustration | Treatment options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade I (Mild) | Early, but perceptible thinning of the hair on the crown |

|
Medical treatment or Mesotherapy |
| Grade II (Moderate) | Pronounced thinning of hair on the crown + noticeably diffuse thinning of hair |

|
Hair Transplant, if hair at back and sides of scalp are stable |
| Grade III (Severe) | Near total denudation on the crown + Severe generalized thinning of hair |

|
Hair Transplant, if hair at back and sides of scalp are stable |
How to prevent hair fall and strengthen the existing hair?
First consult a Dermatologist or Trichologist to pin-point the exact cause for hair loss. Always keep your hair clean. It will protect them from dandruff, itching and hair lice, which ultimately results in hair fall. Massage your scalp with lukewarm oil at least twice a month. Never comb your hair when they are wet; the roots of the hair are the weakest when they are wet. Avoid excessive use of hair dryer and let hair dry in natural air for a while. And last but not the least, never underestimate the role of balanced diet, good exercise, measures to reduce stress and cutting down salon interventions.
So what are the hair loss treatment options?
- Medical treatment: Medications serve an important role in both prevention and treatment of hairloss, particularly in the early stage. Minoxidil helps by increasing the blood supply to the hair thus increasing nutrition and stimulating hair growth. Multivitamins and antioxidants which are rich in nutrients like biotin and iron may be added for the desired effects. Drugs like finesteride show definite increase in hair growth and density. Topical peptides are new class of hair strengthening solutions and work in pushing hair from resting and falling phase to growing phase.
- Laser Treatment: is the latest tool in hair restoration which uses Cool Lasers (low-level red laser light) to stimulate hair growth and reduce shedding of hair. It acts by stimulating the follicles on the scalp by increasing energy production. It is absolutely safe with no side-effects.
- Mesotherapy: It is the most advanced and recent modality where multiple microholes are created over scalp using microneedles through a dermaroller technique. Then anti hairloss solutions or stem cell serum or platelet rich plasma is instilled inside the scalp though these microholes for prevention of hair fall and stimulation of new hair growth. It gives exemplary results in 4 to 6 weeks following therapy in the form of new hair growth and strengthened existing hair!
- Surgical treatment: All the above mentioned techniques work temporarily and Hair Transplant remains the only PERMANENT SOLUTION for androgenetic alopecia.
"I knew I was going bald when it was taking longer and longer to wash my face."




